>
University of Sunderland poster for the visiting Fulbright Scholars.
Tim Tate and I have been powering through our stay here at the University of Sunderland in the beautiful northeast of England. This is a blog update of some of the adventure we have participated in whilst on our Fulbright Scholarship to the UK.
The University of Sunderland Glass Centre and the glass roof deck.
Kevin Petrie, Head of the Glass & Ceramics Department
We arrived on Thursday, met at the airport by the University’s head of the Glass and Ceramics Department, Kevin Petrie. Kevin took us on a whirlwind tour of the massive building complex. The centre, built in 1998, has a glass panel roof – where one is invited to walk across and watch the blowing facilities down below.
Tim Tate takes a walk on the glass.
The size, equipment and state-of-the-art facility was overwhelming. It was great to see some old friends that had come to DC in years past waving a welcoming hello from across the acreage of studio space. We would be coming back to the University after a couple workshops in town.
Some of the many huge kilns at the university.

The beach in front of the hotel in Seaburn.
Our hotel could not have been better – sweeping views across the North Sea, with Seaburn beach in front of our hotel. Nice.
Creative Cohesion’s new studio and exhibition center in Sunderland.
The arts organization, Creative Cohesion, held a cocktail reception to welcome us and inaugurate the new hotshop at their new facility in Sunderland city centre . For those of you from DC, you might remember the organization and its many talented artists that participated in the 2006’s Glass 3 exhibit in Georgetown, organized by Artomatic. In 2009, many more artists from Sunderland participated in the Artomatic held near the Navy Yard/near the new Nationals Ballpark. The non-profit arts organization began over 10 years ago, initially designed as a way to help for glass artists coming from the university mature into professional artists. The success of the organization’s mission has expanded and now includes ceramic and visual arts, performance artists, and poets in its umbrella of services.
Our arrival coincided with the center’s celebration of the opening of their new hotshop – our workshop would be the first for the glass shop. Upon arrival – we see a familiar face – a poster of the UK artists working in Dave D’Orio’s DC Glasswork’s hotshop is in the window.
The artists from Sunderland listen with intent.
The big burly electrician Richie tries fusing for the first time. And shows real talent.

Roger Tye gets the glass into shape.
The next day, Tim Tate and I were welcomed at the University of Sunderland. We first gave a lecture about our work, the Washington Glass School & Studio and the Glass Secessionism movement.
Professor Tim Tate speaks about his work and influences.
Coming up soon – a posting or two about the workshops at the National Glass Center, touring around the area and the London Affordable Art Fair! Stay posted!
Welding Class Just Added!
>
To keep up with the demand – we have just added another welding class to the schedule:
Class 1203-B – Beginning MIG Welding
Ever wondered about learning to weld? Want to impress your friends, your older brother and that cute bartender? It’s easier than you think! In three evenings you will learn how to lay a bead, and handle all sorts of sharp and dangerous tools. You will be able to complete a small project and leave with lots of ideas and know-how for other projects. This class will teach you the basics of welding, metal work and design, joining, bending and finishing. And you will get dirty!
Instructor : Erwin Timmers
Dates : Wednesday evenings in May (2, 9, 16)
Time : 7:00 pm to 9:30 pm
Tuition : $325 per student
This class does not have a paypal button…..contact Erwin directly at 202-744-8222 to register, or email to: washglassschool@aol.com
Ginny Ruffner: A Movie & A Show
>Multimedia artist Ginny Ruffner‘s artwork is an exuberant, mind-blowing party. No matter whether her medium is glass, paint, metal, or paper, the result is a kaleidoscopic explosion of color and form that blurs the lines between indoors and out, natural and mechanical, dream and waking.
Ginny lives and works in Seattle, WA. Despite a life interrupted by a near-fatal auto accident in 1991, Ginny’s years of painstaking recovery have been richly productive.
On Wednesday, February 29, 2012 at 12:00 noon the Renwick Gallery of the Smithsonian American Art Museum will screen “Ginny Ruffner: A Not So Still Life ”, a movie that peers into the kaleidoscopic mind of American glass artist Ginny Ruffner. The documentary explores Ruffner’s journey from her childhood in South Carolina to her emergence as a world-renowned artist. The film also highlights her influences, including Dale Chihuly, Graham Nash, and Tom Robbins. The film is 80 minutes in length and was directed by Karen Stanton.
The event will take place at the Grand Salon of the Renwick Gallery and admission is free. After the screening, Ginny will participate in a discussion about the film and sign copies of the DVD that will be available for purchase on site.
Ginny Ruffner: Works On Paper
Following screening of the film, Maurine Littleton will feature an exhibition of Ginny’s new work, including Ginny’s new works-on-paper at the gallery.
The gallery event will begin at 2:00 PM and Ginny will be present. The Maurine Littleton Gallery is located at 1667 Wisconsin Ave NW, Washington DC.
Also on exhibit are Jeff Zimmer‘s new layered glass works in the upper level gallery space.
Kiln-formed Glass & The American Studio Glass Movement – A Parallel History
>
2012 marks the 50th Anniversary of the American Studio Glass Movement, and its celebration will be marked with many events and exhibitions. The focus of the anniversary celebrations will mainly be on hot-glass and taking glass making from the factory to the artist’s studio, using the 1962 Toledo glass workshop as the birth date.

Toledo glass workshop in the spring of 1962
Horizontal/Vertical, 1974. Harvey Littleton. Chazen Museum of Art, Madison, Wisconsin
Early Fused Glass
While the precise origins of glass fusing techniques are not known with certainty, there is archeological evidence that the Egyptians were familiar with basic techniques. Some historians argue that the earliest fusing techniques were first developed by the Romans, who were much more prolific glassworkers. Fusing was the primary method of making small glass objects for approximately 2,000 years, until the development of the glass blowpipe largely replaced fusing due to its greater efficiency and utility.





___________________________________________


Michael and Francis Higgins’ were a husband-and-wife team who produced commercial tableware for Dearborn Glass.Both studied at the Chicago Institute of Design. The couple individually created unique hinged boxes, mobiles, flat panels and vessel forms that were distinguished by bold geometric patterns and innovative techniques that retain their freshness with their delicate designs.


___________________________________________

Archangel, 1956. Erdis Eckhardt
cast glass. Corning Museum of Glass

Uriel, 1968. Erdis Eckhardt
cast glass. Corning Museum of Glass


1944 Craft Horizons and 2012 American Craft Magazine
Early books about glass offered technical advice, a general history of glass, or the occasional survey of contemporary work. Information about glass was available only in industrial manuals, amongst them “The Art of Glassmaking” (1947) by Sydney Waugh, a designer for Corning Glass. Waugh’s book included declarations that glass could only be made in large factories.
California artist Kay Kinney studied glazes and ceramics and later experimented with glass in the early 1960’s. Kinney’s book “Glass Craft: Designing, Forming, Decoration” (1962) was written long before the “fusing-compatible” era. Her book has information about mold-making, fusing and slumping projects utilizing window glass, bottles, and other types of glass.

Kinney’s book was written for glass novices, with simple, straightforward instructions on cutting and fusing.
Click HERE to jump to Part 2 Exploring Technique and Content – the ’60’s, ’70’s & ’80’s
♪ Happy Birthday, Mr President ♫
>
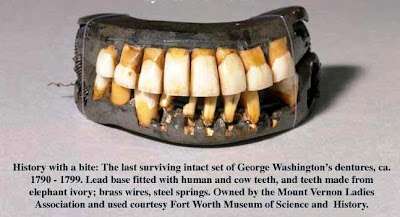
George Washington’s dentures
George Washington FUN FACTS
–Admiring biographers make much of the fact that
–When the capital was moved from
–One of the most seriously misleading of the

In 1842, Abe was challenged to a duel. Abe won.
Abraham Lincoln FUN FACTS
—
–In 1842,
–The clutter in
–Frederick Douglass, the celebrated black abolitionist and former slave, was invited by
–Once, shortly before his election to the Presidency,
Presidential trivia facts from: www.trivia-library.com
Recycled Glass: Sculpture and Design
>

There are some great works and images of projects, including works by DC area artists Nikki O’Neill, Bill Hess and Cindy Ann Coldiron.

“Glass on Stone”
Erwin Timmers, 120″ x 20″ x 2″, kiln cast recycled window glass
photo by Anything Photographic
Our Erwin Timmers‘ environmental themed artwork has an attractive spread in the book. Erwin’s work has been in a number of art book publications this past year – his work has become increasingly popular. Erwin will be showing at Cincinatti’s Brazee Street Gallery in March.
Australian artists that work in recycled glass are also featured in the book – including some spectacular projects by Mark Wotherspoon. Mark reclaims glass from television tubes and creates evocative figures from the hard glass.

“Revelation of Death”
Mark Wotherspoon, 6′ x 8′ x 8′, kiln-cast television screen glass
Have a look at this fascinating look at artists that are looking to create environmentally sustainable artwork.
Who Loves You, Baby? Feel the Love.
>

Smackdown! Lionell VS Rick VS Kojack
The Process – Erwin Timmers Cast Glass Bottles
>
From This:
As part of the ongoing series titled ” The Process” that documents the methodology of an artist or technique – the work of Erwin Timmers is the feature of today’s pictorial.
Eco-artist Erwin Timmers creates artwork with environmental themes, and he works with materials that are diverted from the waste stream. As he prepares for the upcoming Smithsonian Craft Show, he invited us to have a look at how he starts the casting process as he creates his beautiful glass sculptures.
Working within his concepts of sustainable design and art, Erwin sourced glass from the US Probate Courthouse, in Greenbelt, MD for his artwork that was slated to end up in the trash dump.
Using plastic bottles cleared from the Anacostia River watershed (of which there was plenty to choose from), Erwin coats the bottles with a plaster/silica coating.
Using plastic bottles cleared from the Anacostia River watershed (of which there was plenty to choose from), Erwin coats the bottles with a plaster/silica coating.
Erwin extracts the remains of the plastic bottles from the molds.
Erwin then takes the cleaned molds and sets them in a bed of sand inside the glass kiln.
Erwin loads the cleaned glass into the reservoirs and sets the kiln.
After the firing, the glass is divested from the plaster and polished.
Flameworker Simone Crestani
>
Them!

The glass will ultimately be filled with neon and charged.
The glass bug anneals at the glass school – shown here sleeping on a nice soft bed of fiberfrax blanket.

Things are all great – until the bug gets all aggressive and charges Rob. Oh, the humanity!
Class Photo: Intermediate Glass Course
>
The “Next Step” fused glass class is well underway, with the students going large. This week, the artists were engrossed in making pattern sheet elements for a large panel fused work. Balance of color, reactions within colors, working with frit powders, stringers and sharpened cutting skills are the mainstay of the class.
Sifting frit glass powder onto glass allows creation of very detailed glass elements.
More of everything is the class motto!.
The day’s work is loaded into the kiln.
Next week’s installment includes creating even larger panels, as well as cutting perfect circles in glass. Can’t hardly wait!.























