>
Our master of sustainable design, Erwin Timmers, is getting his glass balls polished and ready for display at the Smithsonian Craft Show. This show is the 30th Anniversary of what is often referred to as the premier juried show of fine American Craft Art, running April 19 – 22, 2012, with a Preview Night Benefit on Wednesday, April 18, 2012.

Erwin will be interviewed by WUSA9 anchor JC Hayward. The two will be discussing the Smithsonian show held at the National Building Museum and how Erwin’s sculptural work references environmental issues. His interview will be during the 9 News Now At Noon (slotted between “The Price is Right” and “The Young and the Restless”)
Click Here to jump to the Smithsonian Craft Show website.
Smithsonian Craft Show
April 18 – 22, 2012
Erwin Timmers – Space 503
National Building Museum
(Judiciary Sq. Metro – Red Line)
401 F Street, NW
Washington, DC 20001
ART-O-MATIC Registration Opens!
>
Registration is Now Open for Artomatic 2012!
Registration is now open for artists and performers to display work at Artomatic, the DC area’s biggest free arts festival!
(It may take a bit to get thru – the number of artists rushing to the site had overwhelmed the server on the first night – but there are plenty of spaces!)
Get Yer Art On!
Happy Easter to Our Peeps
Kiln Formed Glass History – Part 2
>

Untitled sculpture, Mary Shaffer, fused and slumped industrial sheet glass, 1975
As part of the 50th Anniversary celebrations in honor of the 1962 Toledo Glass Workshop, the Washington Glass School blog is looking the heritage of the art movement. This is the second part in an historical overview of how fused glass (aka kiln-formed, or warm glass) fits into the contemporary Studio Art Glass Movement. Much of the information was based on published writings by Martha Drexler Lynn, William Warmus & Beth Hylen, Richard LaLonde, Dan Schwoerer & Boyce Lundstrom and from the Corning Museum of Glass library.

Clipped Grass, Mary Ann “Toots” Zynsky, green tinted fused and thermo-formed glass threads, 1982
Antique collecting in the 1960’s brought about a renewed interest in stained glass. Cities such as

The modern stained glass movement, started by mimicking the traditional work evolved into a very diverse art form. Boyce Lundstrom, one of the founders of Bullseye Glass Company wrote:
“Our experience in the glass world pointed to a need for more colored sheet glass for the stained glass industry…(I) began working with glass in 1965, when I joined the new glass program established by Dr. Robert Fritz that year at
In Dr. Fritz’s program I learned to control all phases of the process of making finished blown objects. We built glass melting equipment, calculated and melted batch, formed the glass, and carried out all the cold working processes for finishing the annealed work. After my graduation from
Two of those artists were Ray Ahlgren and Dan Schwoerer, who were partners in a glass blowing. (Ray Ahlgren started his glass career in

Ray Ahlgren, fused glass tiles, plywood, 1982
Said Boyce: “For the next four years, the pressing demands of an infant company consumed all of my time. In 1978 I began designing independent stained glass panels, executed for me by more capable craftspersons. Since, at Bullseye, we produced mixed colors of glass daily, and had control of the formulas, it seemed a foregone conclusion that we could make sheet glass with similar coefficients of expansion.

Boyce Lundstrom, red glass fused bowl, 1979
The thought process went something like this: if sheet glasses had the same coefficient of expansion, they could be cut into shapes and fused together. So, I started experimenting in 1979 or 1980–I don’t know exactly when because the process was slow at first, fraught with many failures and just a few successes. If there was one memorable breakthrough, it was the application of the method of testing for stress with a polarimeter (from glass blowing) to glasses fused to a clear sheet glass with a constant coefficient of expansion.
When making sheet glass it is not important to have a constant coefficient of expansion among all the glasses. Single colors can all be different and mixed colors only have to be within one or two coefficient points of one another. In glass blowing it is not uncommon to use glasses together that vary in coefficient of expansion by four or five points, because the casing process holds the glass together. But when fusing glass flat, the glasses must be very close in coefficients. Establishing a clear glass as a constant, and then formulating the melt for all colors to fit that constant, made the contemporary glass fusing movement possible.
The ability to fuse glass, by taking it through the complete process of heating, holding and annealing, then checking the finished results with an accurate test, really stimulated my dreams of unlimited possibilities. I saw kiln fired glass as the wave of the future, providing freedom for all those who would like to be freed of the lead lines! Tiles, windows, bowls, sculptures, and building facades could all be made with fused sheet glass… By 1981, I became adamant about producing glass for the fusing market at Bullseye Glass. My remaining partner, Dan Schwoerer, supported me in my one-man campaign to make fusing available to everyone. During the next few years we succeeded in making available a line of fusing compatible glasses. By 1983 we were teaching fusing in diverse parts of the world, establishing a line of products and working with kiln manufacturers to get kilns designed for glass on the market.”
The influence by the hot glass education and artwork by the artists that came from the universities now teaching glass artwork outlined the directions that warm or kiln-formed glass would take. In the late 1960s there was the emphasis on technology and education. The glass artwork was part of broader international craft movement of the 1960s in which clay, fiber, wood, and metal are used for creative expression.

Gyes Arcade, Christopher Wilmarth, flat and curved plate glass elements, 1969
In 1969, glass was rarely seen in contemporary art, especially in large-scale sculpture. However, the American Studio Glass Movement was gathering national momentum. Many studio glass artists looked at contemporary sculpture, such as Gyes Arcade, for inspiration on how glass might be treated artistically.
At the 1972 National Sculpture Conference in Lawrence, Kansas, Harvey Littleton introduces his phrase “Technique is cheap” that continues to influence artists. The dichotomy between the sculptor in search of form (the “technique is cheap” attitude) vs. the craftsman striving to create a perfectly executed functional object is a strong motivation for many artists.
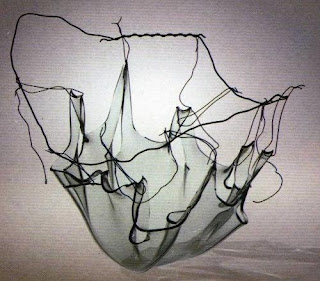
Bowl #2, Mary T Warren, glass, wire, 1978





UK Hosts 2nd International Symposium of Architectural Glass
>
The UK International Institute of Research in Glass (IIRG) presents the 2nd International Symposium in Architectural Glass, focusing on ‘Working with light as a means of interaction between space and the mind’.
The emphasis of this event is on how flat glass is used three dimensionally in space and as a creative means of expression. This will explore both the theoretical and practical aspects of this process: idea exploration; design development; use of new technologies; the possibilities of technical restrictions; and the multi-disciplinary approach prevalent in many projects.
The Symposium will run on Thurs/Friday, May 17 &18, 2012 at the National Glass Centre in Sunderland, England. The event will take the form of traditional lectures, panel discussions, workshops demonstrations and informal networking opportunities. Speakers include:
Marian Karel
Dana Zamecnikova
Judith Schaechter
Algirdas Dovydenas
Daan Roosegaarde
Rodney Bender
Tim Macfarlane
Alexander Beleschenko
Early bird fees, if you book and pay before the 1 May:
One day £55, Two days £90
You can book your place through the University online shop, just search Conference/Events International Glass Symposium.
http://onlinestore.sunderland.ac.uk
University of Sunderland, National Glass Centre
Liberty Way
Sunderland, UK, SR6 0GL
Fulbright Scholars Janis & Tate Final Report
>Final Report by Michael Janis and Tim Tate regarding their Fulbright Specialist Program at the University Of Sunderland and the National Glass Center.
The bonds that were forged years ago when The City of Washington & Washington Glass School hosted the UK artists from Cohesion Glass Network art Artomatic’s Glass 3 event in Georgetown have been strengthened. Our connection with Washington, DC’s UK Sister City, Sunderland, the National Glass Center and the University of Sunderland; will continue throughout our careers. While our mission as Fulbright Scholars was to impart information, we leave having learned many lessons.
Our time in England began with presentations of our artwork and discussions of on new directions the glass world was embracing, such as Glass Secessionism, where artists are looking to move from the aesthetic of pure technique, materials and process and are advancing glass as a medium of sculptural expression in the narrative realm. The participants in the audiences came from the student body of the University as well as working artists from Sunderland, Newcastle, even as far away as Edinburgh, Scotland. The audience stayed long after the talk, and topics from the discussion continued to come up during our entire Fulbright program stay (and indeed, afterwards via the internet) showing the strong relevance of the concepts.
We created workshops for both the National Glass Center and Sunderland’s Creative Cohesion studio; the city’s artist incubator (that, in fact, used the Washington Glass School as its educational and business model). The City of Sunderland invited us to speak with students at a local secondary school during our stay, where we talked about careers in art. We also worked with the Leaders of the University’s Glass and Ceramics program and outlined methods we could extend the cooperative agreement that exists between Sunderland and Washington, DC.
The British tertiary arts education system is different from the US university model. Their MA program blends an MFA and BFA into a very concentrated program. The amount of expertise, materials and techniques they make available to students seems staggering. Sunderland’s may be the finest glass program in the world. With the National Glass Center, the physical space alone dwarfs any facility in the US (or even if one combined the arts centers of Pilchuck, Penland, Corning into one place). The University of Sunderland also offer a doctorate in glass, which is similar to an MFA, though the focus is research, as this is one of the primary methods for the University to receive funds. At the end of a student’s time at Sunderland University, they have a much broader base of knowledge regarding glass and its parameters. In many ways the educational system in the UK is ahead of the US, especially in how they treat glass sculpturally.
Our talks with the students included observations on the differences between the art practices of the two countries. The gallery/collector focus on technique driven vessels that drove the US Studio Glass Movement for over 40 years did not occur to the same extent in England. Instead of being gallery driven, the UK arts education sector seems to be more exhibition and grant driven. University and museum -sponsored art shows are more common as the way an artist would establish themselves. With this as their foundation, artists do not find it as necessary to focus on a single form. They are able operate with the freedom of each installation being potentially a different medium, voice, direction (though many times I would have liked to see the directions pushed much further.) In the US, with the galleries / collector based system, there exists the perception that an artist’s work be recognized for a particular form and for the work be within a series format.
The courses we held at the University included a mix of graduate and undergraduate students, and the workshops allowed and encouraged students working in different modules to interact. We found the students of the University to be some of the most engaged and accomplished students we have ever worked with. They wanted to absorb as much information as possible. Their energy was refreshing, and we added another workshop and added one talk more into the schedule.
Our final discussion was on Artist Covenant’s and how artists can create a network using social media as a way to support each other as a group. This informal talk was packed, standing room only. The artists were voracious in seeking advice on how to get their work seen and recognized. We hope we have helped energize them and perhaps rally them to work together towards their common good. The interest and respect we received from the students was over-whelming. Many of the artists have connected to us online.
We would like to thank all those who made this academic interaction possible: The Fulbright Commission, the Council for International Exchange of Scholars (CIES), The University of Sunderland and the National Glass Center, The City of Sunderland and Creative Cohesion. Each in their own way has made our visit into a life changing experience.
Our mission is to now to reflect and contemplate on not only what we have achieved, but to think of ways on how best to extend our hand and continue our symbiotic and synergistic relationship so that it will not only survive but thrive.
Lets all bridge the Atlantic for many more decades.
Tim Tate & Michael Janis , Co-Directors, Washington Glass School
Dinner with the Board of University of Sunderland and More Workshops!
>
Artist Jeffrey Sarmiento popped into the University of Sunderland’s Architectural Glass studio where our Fulbright workshop classes were being held with an invitation to show how he uses the National Glass Center’s waterjet to cut intricate and delicate glass elements for his artwork. Naturally, I was excited to see 1.) how the waterjet works and 2.) Jeffrey at work.
Jeffrey Sarmiento and Michael Janis
Jeffrey offered to make one of the component layers for the demo piece I was using to show how the sgraffito process can be achieved in glass, and he explained the process. We looked thru some of his images that were in the computer to save time, and selected one of his images of the nearby Tyne bridge that was part of his series “Invisible Cities“.
Jeffrey checks on the initialization of the process.
The pressurized water cuts through the glass and wood support panel.
The grit overflow tub.
The compressor unit located beyond the waterjet machinery.
The verticals of the waterjet cut Bullseye glass panel section are 3mm (less than 1/8″) thick.
Jeffrey pulls apart and assembles the positive and negative.
The connector nibs are pulled off each element.

The panels section loaded and fused in the kiln.
The fired panel integrated into the demo piece.
Washington Glass Fulbright duo of Michael Janis & Tim Tate (plus Kay Janis as chaperone) soldiered on with dinner at the National Glass Centre, hosted by the University of Sunderland Board of Directors. The food at the dinner was a treat – my first Yorkshire Pudding. I was told that Yorkshire pudding and was told the story that the origins of the dish was to provide a cheap way to fill the diners – thus stretching a lesser amount of the more expensive ingredients as the Yorkshire pudding was traditionally served first. The dinner was nothing but elegant.
L-R Fulbright Scholar Tim Tate; Graeme Thompson, Dean of Faculty of Arts, Design and Media; Dr Kevin Petrie, Leader of Glass & Ceramics; (not shown in photo Shirley Atkinson, Deputy Vice-Chancellor; Peter Fidler CBE Vice Chancellor & Chief Executive and James Bustard, Director of the NGC).
The Yorkshire Pudding served.
L-R Cathy Barnes, Chair of the NGC Board; Kay Janis; Chris Jobe, Governor of the Board
Though not “lite” in the sense of calories, it was a delectable, light dessert that was served.
It was a lovely, fun evening that was filled with discussions on how we can create opportunities in both countries that would facilitate the exchange artists, ideas and ways we can strengthen the relationships we have developed.
We had time for one more workshop, held at Sunderland’s not-for-profit artist center, Creative Cohesion. This was to be a much more casual workshop, more a conversation – about the differences in the perceived US and the UK approach towards art and education, the changes that social media had on the art world, how artists can survive in tough economic times, the advantages of creating artist covenants.

Anne Tye, the Creative Industries Development Manager at Sunderland City Council introduces Tim and Michael to a packed audience.


The talks were packed with artists from Sunderland, Newcastle – as far away as Edinburgh, Scotland.

Tim Tate tells all.
The evening talk was the last of our scheduled Fulbright Scholar events. Our short project length had us fly out of town the next morning, heading back to Washington very early.
UK Artist profiles Part 3:
Andrew Livingston
Andrew Livingston works as an artist and is also Leader of CARCuos Ceramic Arts Research Center and MA Ceramics Program Leader at the University of Sunderland, The National Glass Center, Sunderland, UK.
Andrew’s work uses a range of media which acknowledges the interface between both traditional practice and new media. His continued exploration aims to challenge and expand contemporary locations in respect of the traditional positioning of ceramics. The integration of digital media and new technologies has become central to his artwork where new media is often positioned and juxtaposed with more traditional elements.
Andrew’s Parallax View series works in creating a fresh perspective on Tullie House‘s porcelain collection and explores preconceived notions of ceramics.
Surfeit 621 621 cast ceramic components, looped video, and drawings made from clay & graphite.
Britannia. ceramic and glass vitrine.

Roger Tye graduated from Manchester Poly in 1975 with a BA(Hons) in 3D Design – Glass and Metal. Roger to concentrate his work on sculptural and installation pieces that integrated glass and other media. Roger is the guiding force of the new not-for-profit artist studio – Creative Cohesion, located in Sunderland. Though Roger often works in creating beautiful traditional blown glass forms, he also works with slate and cast glass.

glass and slate
cast glass sheep, slate and steel
Click HERE to jump to first posting about the Sunderland trip.
London Affordable Art Fair & Imagery In Glass
>
The first big workshop, Bas-Relief dry plaster casting at the UK’s National Glass Center had gone well (phew!) The Sunderland arts organization, Creative Cohesion, was participating in the London Affordable Art Fair and had invited Tim Tate and I to exhibit our work in the contemporary art show. Which we readily agreed. Tim, my wife Kay & I jumped on a train down to London, and joined the exhibitors at the fair that had opened a couple of days earlier.
Kay Janis watches the North Sea whizz by on the train to London.
Crowd watching is part of the fun of an art fair and at London AAF it included celebrity-sightings of Johnny Depp and Joanna Lumley (Joanna looks loverly, BTW)
Tim Tate’s artwork was featured in the Creative Cohesion Booth.
L-R Dinner with the Creative Cohesion artists Kay Janis, Tim Tate, Robyn Townsend, Joanne Mitchell, Roger Tye, Anne Tye
Tim Tate tuckered out on return train trip.
Our time in London was too short, soon we were back on the train to Sunderland, and preparing for my multi-day class “Imagery in Glass” that was held in the Architectural Glass Studio of the National Glass Center.
Outlining the basics for getting detailed imagery into fused glass.
Showing the different glass powder tools and how an artist can manipulate imagery.
The master level class is tasked with creating a number of sample panels.
Students drew inspiration from the view over the river.
The first firing of glass powder imagery.
Reviewing fused glass samples with class.
Discussing options for creating effects within the layered imagery.
Jeffrey Sarmiento created a component layer for the class demo project – the artwork suggests creating bridges between the art communities.
Jeffrey Sarmiento was recently appointed Reader in Glass at the National Glass Center at the University of Sunderland. A Filipino-American artist, he holds an MFA in Glass from the Rhode Island School of Design. His research has led him to work widely in the US and Europe, having been awarded a Fulbright Scholarship Denmark. He was also a finalist for the Louis Comfort Tiffany Award and the Bombay Sapphire Prize. His most recent project is a 600kg glass map, permanently housed in the new Museum of Liverpool.
Liverpool Map Jeffrey Sarmiento and Inge Panneels, 2010
Bombay Encyclopedia
Jeffery Sarmiento talks about his work “Ossify”
Ossify 2010 British Glass Biennale Award Runner up

Emotional Leak Jeffrey Sarmiento & Erin Dickson, 2011
Cate Watkinson trained in 3-D Design, Glass with Ceramics at Sunderland Polytechnic.After leaving college Cate worked in Cambridge and the Channel Islands before returning to the North East to set up her architectural glass studio. Cate continues to run her business, Watkinson Glass Associates, while teaching at the University of Sunderland.
Over the years Cate has built on her experience, optimizing developments in new technologies, including new developments and techniques in construction. She has successfully completed a varied range of commissioned projects from glass public seating in city centers to a 22’ high sculpture for a shopping mall. From a stained glass window for Newcastle Cathedral to a laminated glass screen for the Arrivals Hall at Newcastle International Airport in the UK.
Other research activities include exploring the use of text and light through the public art commission entitled `Total Policing’, a glass and stainless steel sculpture situated at the front of the new head quarters for Northumbria Police in North Tyneside.
Total Policing
Baltic Business Quarter Public art/seating made with recycled glass.
Lookout
Next Up – Creative Cohesion artist development talk, dinner with the Uni Board, and more great UK artists!
Fulbright Scholars at University of Sunderland
>
Our Fulbright schedule began to fill the days.The first workshop we held at the University of Sunderland’s National Glass Center: “Affecting Sheet Glass – Bas-Relief Imagery in Glass” was filled. The technique of “dry plaster casing” was outlined, and firing schedules were converted from Fahrenheit to Celsius – along with converting all dimensions from imperial to metric. (Why did the US decide to not join the world in the 70’s when we were supposed to go all metricationed?)
Tim Betterton sets up the kilns for dry plaster casting.
After the firing, its like Christmas day as the students eagerly retrieve their kilnformed glass sculptures.
We were able to meet a number of incredibly talented artists that were associated with the University and their work was so strong that we will post some of the work and profiles about the artists in each of the next few blog updates:

Dr Kevin Petrie leads the Glass and Ceramics department at the University of Sunderland. Kevin studied Illustration at the University of Westminster and Ceramics and Glass at the Royal College of Art. He holds a PhD in ceramics and print from University of the West of England, Bristol. Kevin’s first book ‘Glass and Print’ established the crossovers between Glassmaking and Printmaking. The book forms the cornerstone of a period of research that established the cross over between two largely separate strands of creative activity. His second book, ‘Ceramic Transfer Printing’ draws together the great potential of print for ceramics. Kevin has written many articles and reviews for journals such as Ceramic Review and presented his work on glass, ceramics and print in Canada, Thailand, Hong Kong, Denmark, Germany, USA, Australia, and China. He was recently awarded a National Teaching Fellowship for his contribution to glass and ceramics teaching, in particular this relates to postgraduate at MA, MPhil and Ph.D levels.
Dr Petrie’s work often refers to the long tradition of graphic ceramic surface decoration at the same time as reflecting contemporary life.
St Pauls Church, kilnformed glass
Cell of Himself, Kiln form glass with printed inclusions, blown glass
Besides his own work as an artist, Dr Petrie is an author, lecturer, exhibition curator, and he is an authority and specialist on contemporary glass and ceramics matters. He has lectured at the following institutions: The University of the West of England, Bristol, The University of Westminster, London, Norwich School of Art and Design, Bath Central St. Martins School of Art and Design, London, Rajabhat Institute Changmai, Thailand, Australia National University, Canberra, Australia, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, Sydney College of the Arts, Australia, Anla Glas, Denmark, Hong Kong Baptist University – Academy of Visual Arts.
__________________________________________________________

If you are familiar with the first of the DC / Sunderland glass exhibition “Glass3” that was held in Georgetown in 2008, you might have seen James Maskrey‘s work. His work has really transformed into haunting and ethereal work. Social situations, overheard conversations, observed interactions and personal experiences hugely inspire Jim’s work. Tall stories, elaborate hoaxes and peculiar facts, usually from a bygone era, are then translated into glass, often resulting in flamboyant narratives, theatrical compositions or simple objects with a twist. The series below are from a series based on the polar expeditions by Edward Wilson to collect penguin eggs.
The Worst Journey in the World, blown and hot sculptured glass details, 2011. Photo by David Williams


Last Entry,Winter Journey, andThe Barrier, 2011, Blown and solid formed hot glass with printed glass inclusions.
The works poetically and poignantly touches on themes of collecting and hubris. In the austral winter of 1911, Wilson led “The Winter Journey”, a doomed journey to the Emperor penguin’s breeding grounds at Cape Crozier to collect eggs for scientific study. The eggs were supposed to reveal the evolutionary links between dinosaurs and birds but their collection nearly killed the journey’s participants. Frozen and exhausted, they successfully collected three eggs and desperately exhausted they returned to Cape Evans, later describing this expedition “The Worst Journey in the World.”
James started working with glass in 1990. After graduating in 2000 with a Three Dimensional Design BA (Hons) degree in glass at The Surrey Institute of Art and Design he was appointed as Artist in Residence at the Surrey Institute. In 2001 James joined the Glass and Ceramics department at The University of Sunderland and graduated with an MA in Glass with distinction in 2004. Jim was recently named as one of the artists that will exhibit at the British Glass Biennale 2012.
Coming Next – London Affordable Art Fair & Imagery in Glass Class and featured Sunderland Artists: Jeff Sarmiento, Cate Watkinson and more!
Washington, DC Fulbright Scholars Connect with Ancestral Home of President George Washington
>As our time in the UK continued, Fellow Fulbright Scholar Tim Tate and I were invited to speak with students from St. Anthony’s – a technical specialist college in Sunderland.
Tim Tate & Michael Janis talk about the future of the arts to students at St Anthony’s in Sunderland, England.
After meeting with the students, Sunderland City Council’s Catherine Auld then took the DC crew on a quick jaunt to a couple of scenic spots that are around the city of Sunderland. First stop, the Town Hall and Indoor Market of Durham.
Tim Tate and Kay Janis at the Durham Town Hall.
Durham Town Hall and Market place were on the site since the Middle Ages. The current building dates from 1800’s.
Kay Janis seeks out notions from the indoor markets.
Nearby is the famed Durham Cathedral. The magnificent Romanesque structure dates from the 10th century, and boasts fine stained glass panels.
Durham Cathedral (and denim jeans artwork installation).
Catherine Auld, Kay Janis and Tim Tate at the Cathedral’s famed “Sanctuary Knocker”.

“Daily Bread” stained glass in Durham Cathedral by Mark Angus, 1984.
More importantly, the Cathedral, cloisters and grounds were used as some of the sets in the Harry Potter movie series.


Professor Tate as Harry Potter and the Fulbright Scholar, 2012
The Saxon Origin of the Washington Family Name: This was, in fact, where the purely Saxon name of Washington derived. Among the first to bear it were the descendants of William de Hartburn near Stockton [-on-Tees], who came to live in the manor now known as Washington Old Hall as long before as 1183.
At that time, people in England and elsewhere had no surnames as we know them today, and were most often identified by the locations in which they lived. “Washington” was one of them. The name originally meant “the estate of the Hwaes family.’ “Hwaes” in its turn was the name of a Saxon chief, while “ynga” meant “family” and “ton” – a typically Saxon suffix – stood for “estate.” These three terms were linked and given a tinge of French since, like many prominent families in England, the new Washingtons sought to identify themselves with the French Plantagenet kings who succeeded the Normans and ruled England after 1154. The result was the original form of Washington – “de Wessyngton”.
Washington, DC Fulbright Scholars Tim Tate and Michael Janis pay homage to the Washington Old Hall in Durham County, UK.
Washington Old Hall was pulled down and rebuilt by the Bishop of Durham, who purchased the property from William de Wessyngton in 1613.Sadly, though, some three centuries later, it had become very dilapidated. The Hall was condemned as unfit for human habitation, and destined for demolition. It was fortunately saved from demolition by a committee specially formed to preserve it, and after thoroughgoing restoration work, the Hall was officially opened in 1955 by the then American ambassador, Winthrop W. Aldrich. Two years later, the Hall was taken over by the National Trust, an organization dedicated to preserving places of historical interest or natural beauty.
Garth Clark lecture on Ai Weiwei ceramics
The next morning, Garth Clark, noted art historian and critic – who the Washington Glass School has posted about his thoughts on the Death of Craft previously – gave a fascinating and provocative lecture about the work of Chinese bad-boy ceramic artist Ai Weiwei.
Click here to jump to first part of the Fulbright Journey blog posts.






















